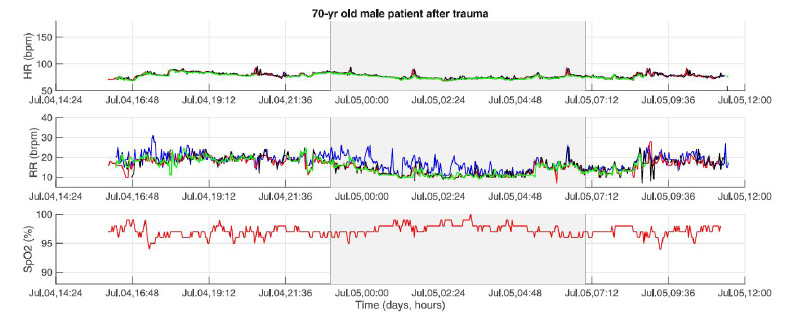
Results:
Twenty adverse events occurred in 11 of the 31 patients included. Atrial fibrillation (AF) was most common (20%). The onset of AF was recognizable as a sudden increase in HR in all recordings, and all patients with new-onset AF after esophagectomy developed other postoperative complications. Patients who developed respiratory insufficiency showed an increase in RR and a decrease in SpO2, but an increase in HR was not always visible. In patients without adverse events, temporary periods of high HR and RR are observed as well, but these were transient and less frequent.
Conclusions:
Current systems for remote wireless patient monitoring on the ward are capable of detecting abnormalities in vital sign patterns in patients who develop adverse events. Remote patient monitoring may have potential to improve patient safety by generating early warnings for deterioration to nursing staff.